The Boundless Potential of Computer Vision
In the realm of artificial intelligence, computer vision stands out as a remarkable field that enables machines to interpret and understand visual data, replicating the human ability to perceive the world. With advancements in deep learning and image processing techniques, computer vision has witnessed unprecedented growth, revolutionizing industries and opening up new possibilities across various sectors.
This article delves into the fascinating world of computer vision, exploring its applications, challenges, and potential impact on society.
1. Understanding of Computer Vision
Computer vision refers to the scientific discipline that empowers machines to extract meaningful information from visual data, such as images and videos. It involves the development of algorithms and techniques that enable computers to perceive, analyze, and interpret visual content, mimicking human visual perception.
By combining image processing, pattern recognition, and machine learning, computer vision systems can recognize objects, detect and track motion, estimate depth, and much more.
Applications of Computer Vision
1. Object Recognition and Classification
Computer vision enables machines to recognize and classify objects within images or videos. This finds applications in various domains, such as autonomous vehicles, where objects like traffic signs, pedestrians, and vehicles need to be detected and classified for safe navigation.
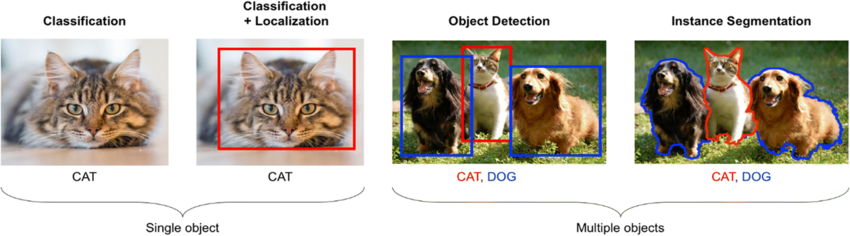
2. Image and Video Analysis
Computer vision techniques facilitate the analysis of images and videos on a semantic level. This includes tasks such as scene understanding, image captioning, video summarization, and content-based image retrieval. Applications range from content organization in large image and video databases to automated video surveillance systems.
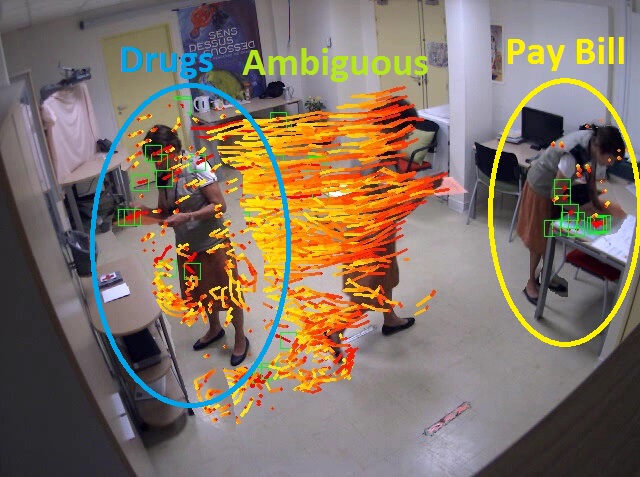

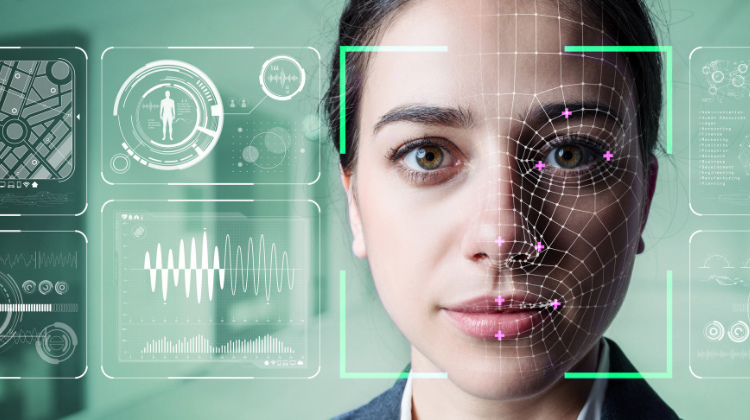
3. Facial Recognition
Computer vision has revolutionized facial recognition technologies. It enables machines to identify and verify individuals based on facial features. Facial recognition is used in security systems, access control, identity verification, and digital entertainment applications.

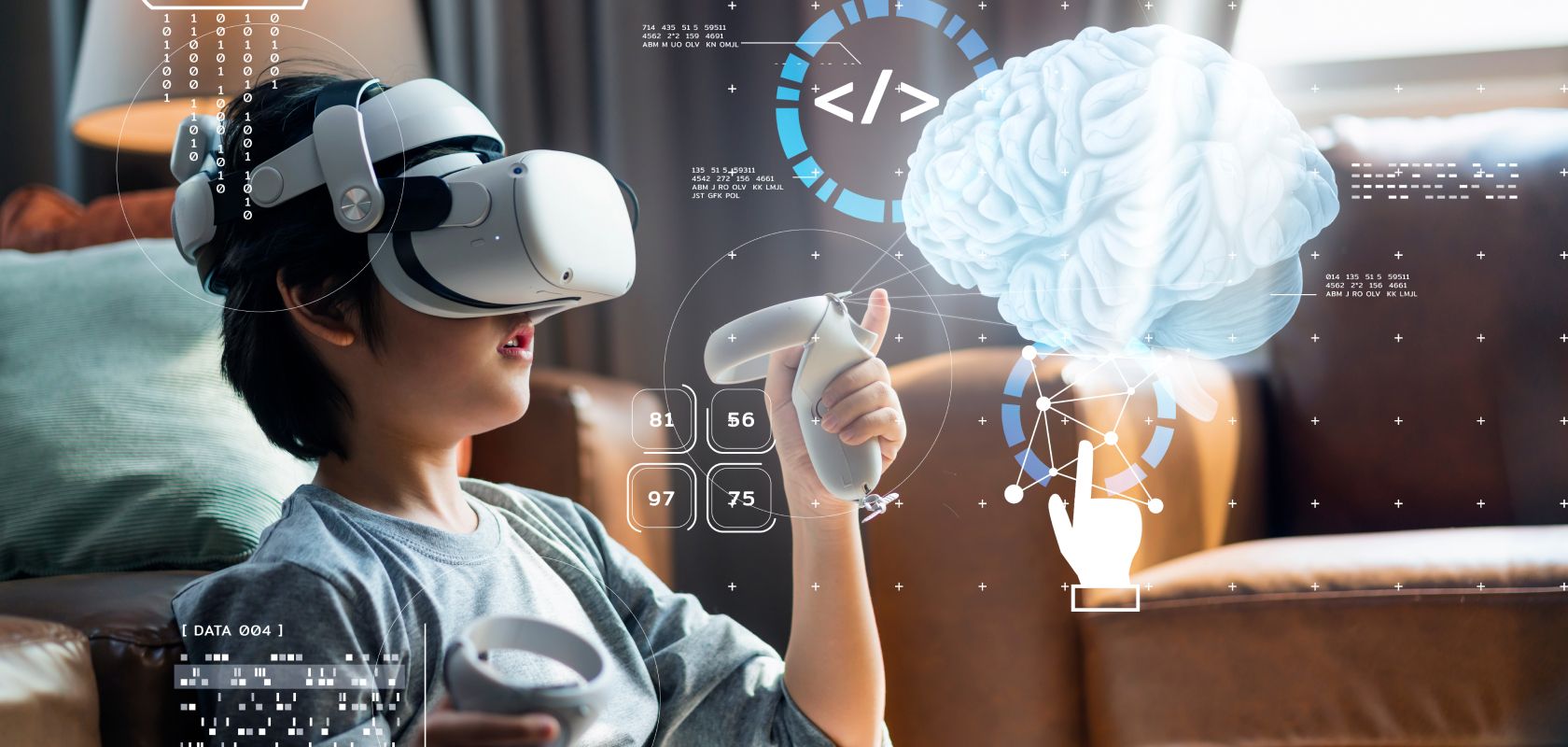
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Computer vision is fundamental to AR and VR technologies. By understanding the real-world environment through cameras, computer vision enables the overlaying of virtual objects onto the physical world, creating immersive and interactive experiences.

5. Robotics and Autonomous Systems
Computer vision plays a vital role in robotics and autonomous systems. It allows robots to perceive and interact with the surrounding environment. Applications include robot navigation, object manipulation, object tracking, and human-robot interaction.
6. Medical Imaging and Healthcare
Computer vision has transformed medical imaging, enabling more accurate diagnosis and treatment. It aids in tasks such as tumor detection, segmentation, and tracking in medical scans. Computer vision also supports image-guided interventions, robotic surgeries, and the analysis of cellular and molecular images.
7. Quality Control and Manufacturing
Computer vision systems are extensively used in manufacturing for quality control and inspection. They can detect defects, measure dimensions, and ensure product consistency and accuracy. This improves efficiency and reduces manual labor in production lines.
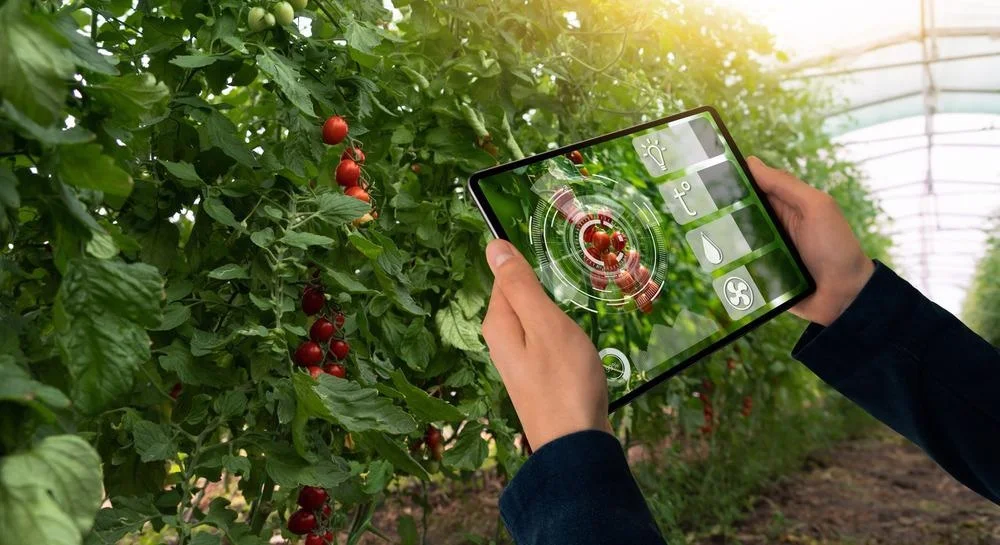
8. Agriculture and Food Industry
Computer vision techniques assist in agriculture and the food industry. They enable crop monitoring, disease detection, yield estimation, and automated sorting and grading of fruits and vegetables.

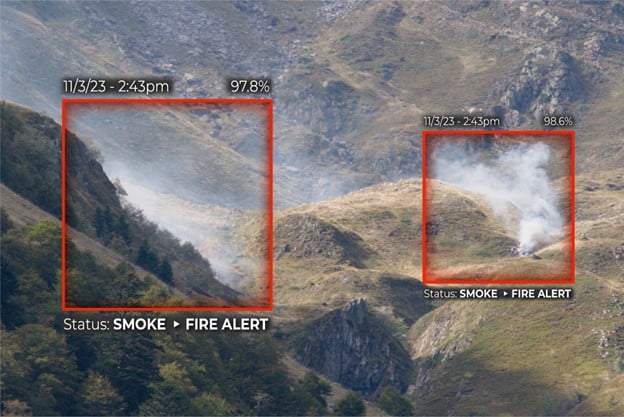
9. Security and Surveillance
Computer vision is employed in security systems for surveillance and threat detection. It enables real-time monitoring, object tracking, behavior analysis, and anomaly detection in crowded spaces, transportation hubs, and critical infrastructure.
10. Human-Computer Interaction
Computer vision enables natural and intuitive human-computer interaction. Gesture recognition, eye tracking, and facial expression analysis allow users to interact with devices and interfaces using gestures, gaze, and facial expressions.
11. Sports Analytics
Computer vision is applied in sports analytics to track and analyze player movements, identify patterns, and provide insights for training, game strategies, and referee decision-making.
12. Environmental Monitoring
Computer vision can contribute to environmental monitoring and conservation efforts. It aids in tasks such as land cover classification, vegetation analysis, species identification, and wildlife tracking, facilitating ecological research and conservation initiatives.

13. Gesture Recognition
Allows machines to interpret and respond to hand movements, enabling touchless interfaces and control systems.
14. Document Analysis
Facilitates automatic text recognition, document understanding, and information extraction for tasks such as document digitization and archival.
15. Retail and E-commerce
Supports tasks like product recognition, shelf monitoring, visual search, and virtual try-on for enhancing customer experiences and optimizing inventory management.
16. Art and Cultural Heritage
Enables the analysis of artworks, authentication, restoration, and digitization of cultural artifacts.
17. Traffic Monitoring and Management
Assists in traffic flow analysis, license plate recognition, congestion detection, and smart traffic light control.
18. Geological Exploration
Analyzes satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and remote sensing data for geological mapping, mineral exploration, and environmental impact assessment.
19. Augmented Assistance for the Visually Impaired
Enhances accessibility by providing real-time object recognition, navigation assistance, and text-to-speech capabilities.
20. Entertainment and Gaming
Powers interactive games, virtual characters, motion capture, and face tracking for immersive experiences.
Conclusion
Computer vision has emerged as a transformative technology with a wide range of applications and the potential to reshape various industries. As advancements continue, it is crucial to address the challenges and ethical considerations associated with this technology.
By leveraging the power of computer vision responsibly, we can unlock its full potential and create a future where machines perceive and interpret the world around us, benefiting society in profound ways.


 EN
EN JP
JP KR
KR