Harnessing the Power of Deep Learning in ERP, SCM, and MES Systems
In the rapidly evolving world of enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), and manufacturing execution systems (MES), businesses are constantly seeking innovative solutions to optimize their operations, enhance productivity, and gain a competitive edge.
One such solution that has gained significant attention and transformative potential is deep learning. This article delves into the realm of deep learning and explores its applications in the context of ERP, SCM, and MES systems, highlighting the benefits and challenges associated with its implementation.
1. Understanding Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on training artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn and make intelligent decisions from vast amounts of data. Through this process, deep learning models can identify patterns, extract meaningful insights, and make accurate predictions or classifications.
2. Enhancing ERP Systems with Deep Learning

2.1 Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting is a critical aspect of ERP systems, enabling businesses to optimize inventory levels and improve customer satisfaction. Deep learning algorithms can analyze historical sales data, market trends, customer behavior, and various external factors to generate accurate demand forecasts.
This empowers organizations to make proactive decisions regarding procurement, production planning, and resource allocation.
2.2 Anomaly Detection
ERP systems handle a vast amount of data, making it challenging to identify anomalies or deviations that may indicate issues such as fraud, errors, or system malfunctions. Deep learning algorithms can be trained to detect anomalies by learning the normal patterns and characteristics of the data.
This enables timely detection and mitigation of potential risks, ensuring the integrity and security of ERP systems.
3. Leveraging Deep Learning in SCM Systems
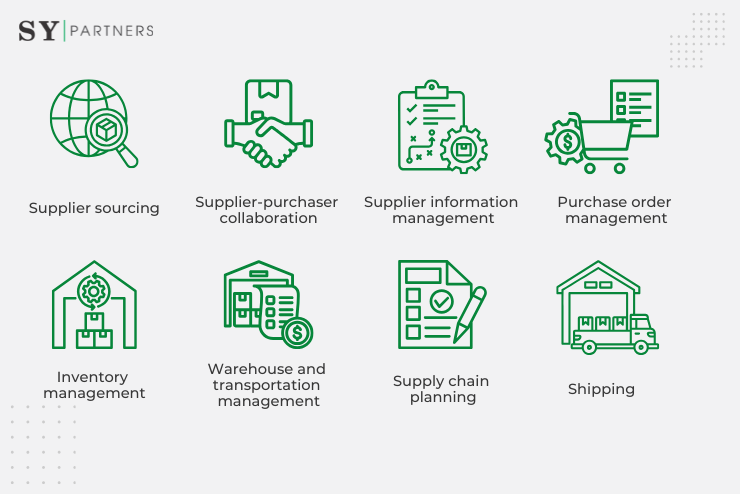
3.1 Inventory Optimization
Deep learning can play a crucial role in optimizing inventory levels by learning from historical data, market trends, lead times, and demand patterns. By accurately predicting demand and dynamically adjusting inventory levels, SCM systems enhanced with deep learning capabilities can minimize stockouts, reduce carrying costs, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
3.2 Route Optimization
Deep learning models can analyze real-time data such as traffic conditions, weather forecasts, and delivery constraints to optimize logistics and route planning. By considering various factors and learning from past patterns, SCM systems can generate optimal delivery routes, reducing transportation costs, and improving delivery timeframes.
4. Empowering MES Systems with Deep Learning
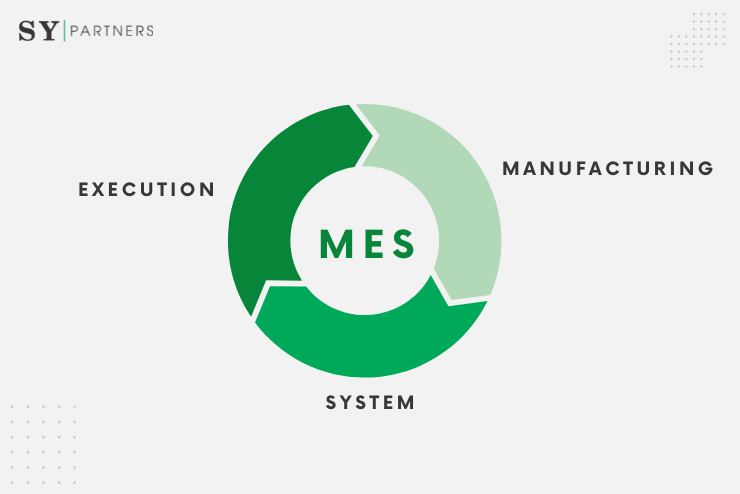
4.1 Quality Control
Ensuring product quality is paramount in manufacturing processes. Deep learning algorithms can analyze sensor data, images, and other relevant data sources to detect defects, anomalies, or deviations from quality standards. By automating quality control processes, MES systems can enhance production efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall product quality.
4.2 Predictive Maintenance
Deep learning models can leverage historical data, sensor readings, and maintenance records to predict equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling. By identifying potential issues before they occur, MES systems can minimize unplanned downtime, optimize maintenance resources, and extend the lifespan of critical equipment.
5. Challenges and Considerations
Implementing deep learning in ERP, SCM, and MES systems comes with its own set of challenges:
5.1 Data Availability and Quality
Deep learning models require large volumes of high-quality data for training. Ensuring the availability and quality of relevant data can be a significant hurdle for organizations.
5.2 Interpretability
Deep learning models are often considered "black boxes" due to their complex structures. Interpreting the decisions made by these models can be challenging, especially in industries where explainability and traceability are critical.
5.3 Infrastructure and Expertise
Deploying deep learning models requires robust computational infrastructure and skilled data scientists or machine learning experts. Organizations must invest in the necessary resources to support the implementation and maintenance of deep learning systems.
Conclusion
Deep learning has the potential to revolutionize the way ERP, SCM, and MES systems operate, offering unprecedented capabilities in demand forecasting, anomaly detection, inventory optimization, route planning, quality control, and predictive maintenance. By harnessing the power of deep learning, businesses can unlock valuable insights, streamline operations, and stay ahead in today's competitive landscape.
However, careful consideration of challenges such as data availability, interpretability, and infrastructure is essential to ensure successful implementation. As the field of deep learning continues to evolve, its integration into ERP, SCM, and MES systems holds the promise of driving efficiency, agility, and innovation in enterprise operations.


 EN
EN JP
JP KR
KR