Limitless Applications of Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation in the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP). These models, based on deep learning and advanced neural network architectures, have the capability to process and generate human-like text, revolutionizing various applications such as language translation, content generation, and conversational AI.
In this article, we will delve into the world of LLMs, exploring their significance, functioning, applications, training methodologies, and the exciting future they hold.
1. What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
Large Language Models refer to extremely powerful deep learning models that are pre-trained on massive datasets. These models utilize transformer architectures, comprising encoder and decoder components with self-attention capabilities. By understanding the relationships between words and phrases within a text sequence, LLMs can extract meaning and generate coherent and contextually relevant responses. The transformer architecture enables parallel processing of entire sequences, significantly reducing training time.
2. Why are Large Language Models Important?
Large Language Models hold immense importance due to their remarkable flexibility and versatility. A single LLM can perform diverse tasks, including question answering, document summarization, language translation, and sentence completion.
Their predictive abilities are becoming increasingly impressive, enabling them to generate content based on minimal input prompts. LLMs have the potential to transform content creation, search engine functionality, and virtual assistant capabilities, enhancing user experiences.
3. How Do Large Language Models Work?
At the core of LLMs' functioning lies the representation of words using multi-dimensional vectors known as word embeddings. Unlike traditional numerical tables, word embeddings capture contextual meaning and relationships between words.
Transformer-based LLMs process text through an encoder, which converts it into numerical representations, and a decoder, which utilizes this knowledge to generate output. This mechanism allows LLMs to produce contextually appropriate and coherent responses.
4. Applications of Large Language Models
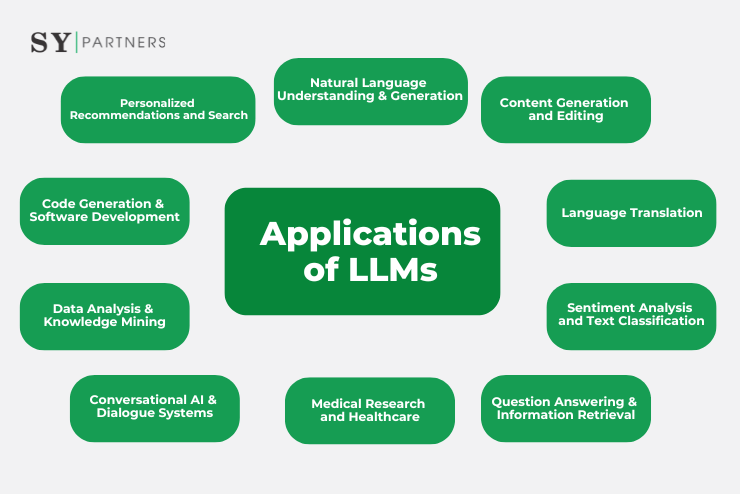
4.1 Natural Language Understanding and Generation
LLMs excel at understanding and generating natural language, enabling applications such as chatbots, virtual assistants, and voice-controlled devices. These models can comprehend user queries, provide relevant information, and engage in interactive conversations, enhancing customer support experiences.
4.2 Content Generation and Editing
LLMs have become powerful tools for content creation, including writing articles, blog posts, marketing copy, and social media content. They can assist in generating engaging and relevant content by suggesting improvements, paraphrasing, and even generating original text based on given prompts.
4.3 Language Translation
LLMs have significantly improved language translation capabilities. They can translate text from one language to another while preserving the context and nuances of the original content. This has facilitated communication across borders and empowered businesses to expand their global reach.
4.4 Sentiment Analysis and Text Classification
LLMs are instrumental in sentiment analysis and text classification tasks. By analyzing the sentiment and tone of text, they can determine whether a piece of content is positive, negative, or neutral. This enables businesses to gain insights from customer feedback, monitor brand reputation, and detect emerging trends.
4.5 Question Answering and Information Retrieval
LLMs have proven to be highly effective in question answering systems and information retrieval tasks. They can provide accurate and relevant answers to specific queries by extracting information from vast knowledge bases and digital archives. This has transformed the way users search for information and access knowledge.
4.6 Conversational AI and Dialogue Systems
LLMs play a crucial role in developing conversational AI agents and dialogue systems. These models can engage in natural and contextually relevant conversations, simulating human-like interactions. They are utilized in customer service chatbots, virtual agents in gaming, and interactive voice response systems.
4.7 Data Analysis and Knowledge Mining
LLMs can assist in data analysis and knowledge mining tasks by extracting insights, summarizing large volumes of text, and identifying patterns and trends. They can automatically process and analyze vast amounts of data, enabling researchers and analysts to derive valuable information more efficiently.
4.8 Code Generation and Software Development
LLMs have found applications in code generation and software development. They can generate code snippets, provide code suggestions, and aid in automating repetitive programming tasks. This improves developer productivity and accelerates the software development process.
4.9 Medical Research and Healthcare
In the medical field, LLMs are used to analyze medical records, research papers, and patient data. They assist in diagnosing diseases, identifying potential drug interactions, and aiding in clinical decision-making. LLMs also contribute to medical image analysis, improving disease detection and diagnosis accuracy.
4.10 Personalized Recommendations and Search
LLMs enable personalized recommendations and search experiences based on user preferences and behavior. By understanding user intent and context, they can provide tailored recommendations for products, services, movies, and more. This enhances user engagement and improves the quality of search results.
5. Training Large Language Models
Large Language Models are trained using massive neural networks with billions of parameters. Training involves iteratively adjusting these parameters to predict the next token in a given sequence of input tokens. Self-learning techniques maximize the likelihood of correct predictions.
LLMs can be fine-tuned for specific tasks using relatively small sets of supervised data, allowing adaptation to various applications. Zero-shot learning, few-shot learning, and fine-tuning methods contribute to the training process.
6. The Future of Large Language Models
The future of Large Language Models holds tremendous promise. Ongoing advancements aim to enhance accuracy, reduce biases, and eliminate incorrect answers. LLMs are gradually moving toward human-like performance, and their introduction has sparked interest in robotic-type models that emulate and surpass human capabilities.
Further developments include audiovisual training, enabling LLMs to process video and audio inputs, and transforming workplaces by automating repetitive tasks and improving conversational AI.
Conclusion
Large Language Models have revolutionized Natural Language Processing, enabling machines to comprehend and generate human-like text. With their versatility, LLMs have found applications in copywriting, knowledge base answering, text classification, code generation, and text generation.
Training LLMs involves large-scale neural networks and techniques like fine-tuning. The future holds exciting possibilities, including enhanced capabilities, audiovisual training, and widespread adoption in various industries, transforming the way we interact with machines and advancing the field of NLP.


 EN
EN JP
JP KR
KR