Types and Features of UI: Comparing GUI, CUI, CLI, VUI, TUI, and NUI
The User Interface (UI) is the point of interaction between users and digital products or systems, significantly influencing usability and work efficiency. For businesses, choosing the right UI is the key to improving user-friendliness and maximizing the effectiveness of data analysis and system management.
This article explains in detail the characteristics, pros and cons, and use cases of GUI, CUI, CLI, VUI, TUI, and NUI. We will also include comparison tables to help companies and developers select the most suitable interface for their purposes.
1. What is a User Interface (UI)?
A User Interface (UI) is the mechanism that connects users with devices or software when performing operations. Buttons, voice input, gestures, and other formats exist to convey the user’s intent to the system and provide clear feedback in return.
In business contexts, the UI of data analysis tools or business applications directly impacts decision-making speed and productivity. For example, a data dashboard UI organizes complex information visually, supporting user understanding and action. Moreover, with the help of AI-based user testing, UI improvements can be identified based on operation logs.
Main roles of UI:
- Provide intuitive operability: Easy to use for anyone at first glance
- Visualize and communicate information: Organize and present complex data effectively
- Improve task efficiency: Reduce operational errors and speed up workflows
UI is an essential element for smooth interactions between users and systems. With proper UI design, not only can operational efficiency be improved, but the overall quality of user experience can also be significantly enhanced.
2. Why is it important to understand different types of UI?
| Importance | Content | Example of Business Application |
|---|---|---|
| Usability | Provides intuitive operation | Improves usability of data analysis tools |
| Learning Cost | Optimizes user learning burden | GUI adoption for beginner-friendly apps |
| Business Applicability | Enables UI selection suited to purpose | CLI utilization for system management |
Understanding the different types of UI is essential for selecting the best interface depending on the project or business objective. Choosing the right UI improves user experience, reduces learning costs, and boosts operational efficiency. For example, GUI enables intuitive operation in data analytics tools, while CLI allows fast and flexible control in system administration.
Furthermore, AI-driven user testing makes it possible to evaluate usability and operability of each UI based on data, supporting rational decision-making in UI selection. Conversely, choosing the wrong UI for a purpose can reduce usability, leading to user disengagement and inefficiency.
Why understanding UI types matters:
- Optimize usability: Provide comfortable operation by matching the UI to goals and users
- Manage learning cost: Minimize the time and effort needed for users to learn the system
- Improve business applicability: Maximize productivity with UI designed for specific use cases
UI selection impacts more than just design or usability—it has a direct effect on business outcomes. This makes it crucial to fully understand the types and characteristics of UI, which ultimately becomes the key to product success.
By understanding UI types, companies can choose the right interface for their objectives, improving both operational efficiency and user satisfaction.
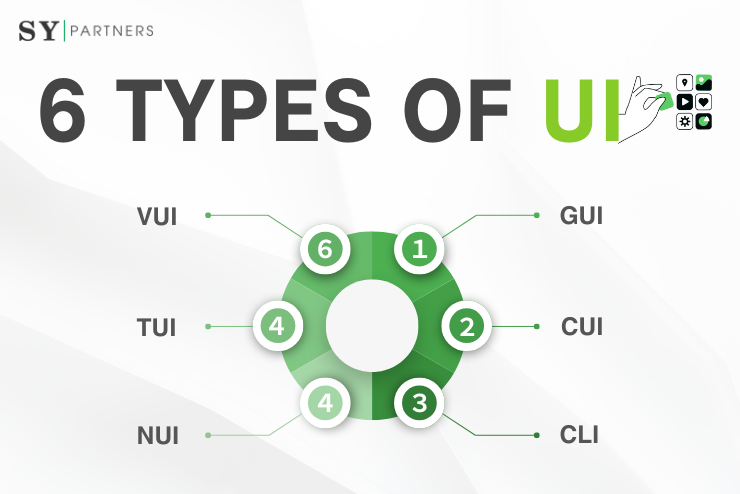
3. Comparison of Different UI Types
By comparing different UI types, businesses can identify the most suitable option in terms of usability, learning cost, and intended application. This section covers six UI types—GUI, CUI, CLI, VUI, TUI, and NUI—highlighting their characteristics and use cases in enterprise settings.
3.1 Differences in Usability
Usability refers to how intuitive and easy a UI is to operate.
For example, GUI is beginner-friendly thanks to its visual elements, while VUI allows hands-free operation but depends heavily on speech recognition accuracy. On the other hand, CLI enables fast operations but requires a certain level of proficiency.
In business, GUI is often adopted for data analytics tools to ensure visual and intuitive interactions, whereas CLI is widely used in server management for speed and efficiency.
| UI Type | Definition/Description | Usability | Example of Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| GUI (Graphical User Interface) | Operated using images, icons, and other visual elements. | Visual and intuitive | Data analytics dashboards |
| CUI (Character User Interface) | Text-only, operated in a conversational style. | Requires command input | Server configuration |
| CLI (Command Line Interface) | Operated by directly typing commands via keyboard. | Fast, but requires training | Script execution |
| VUI (Voice User Interface) | Operated using voice input and instructions. | Hands-free | Smart devices |
| TUI (Tangible User Interface) | Uses physical objects to interact with digital data. | Tactile and intuitive | Educational tools |
| NUI (Natural User Interface) | Operated via natural human actions such as gestures, gaze, or speech. | Natural interaction | AR/VR apps |
Usability is key to UI selection. Companies must align the chosen UI with user skill levels and operational needs to maximize efficiency.
3.2 Comparison of Learning Cost
Learning cost refers to the time and effort required for a user to become proficient with a UI.
- GUI: Low learning cost, beginner-friendly due to visual intuitiveness.
- CUI & CLI: High learning cost, as users must acquire command knowledge.
- VUI & TUI: Moderate learning cost.
- NUI: Medium to high, depending on the complexity of available functions.
In practice, enterprises may introduce CLI for engineers who need advanced operations, while providing GUI for general users to ensure accessibility.
| UI Type | Learning Cost | Example of Application |
|---|---|---|
| GUI | Low | Apps for general users |
| CUI | High | Tools for system administrators |
| CLI | High | Developer-oriented scripting |
| VUI | Medium | Voice assistants |
| TUI | Medium | Educational devices |
| NUI | Medium to High | AR/VR interaction |
Considering learning cost helps businesses design and implement UIs that fit their target users. The balance between efficiency and accessibility is crucial.
3.3 Choosing the Right UI for Each Use Case
UI selection largely depends on business goals and user skill levels.
- Data analytics tools: Best suited for GUI, as visualization supports intuitive use.
- Server management: Best suited for CLI, which allows rapid execution.
- Smart devices: Best suited for VUI, providing hands-free convenience.
- Educational tools: Best suited for TUI, offering tactile learning experiences.
- AR/VR apps: Best suited for NUI, enabling interaction through natural movements.
AI-driven user testing can further enhance decision-making by providing quantitative data on usability and suitability.
| Use Case | Recommended UI | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Data Analytics | GUI | Intuitive visualization |
| System Management | CLI | Fast command execution |
| Smart Devices | VUI | Hands-free operation |
| Educational Tools | TUI | Tactile learning |
| AR/VR | NUI | Natural interaction |
Choosing the right UI based on context directly improves operational efficiency. By aligning UI design with project goals and user characteristics, companies can maximize productivity.
4. GUI (Graphical User Interface)
GUI is an interface that allows users to operate through visual elements. In this section, we will explain in detail the characteristics of GUI and its use cases.
4.1 What is GUI?
GUI (Graphical User Interface) is a visual interface that uses icons, buttons, and windows. Users can interact intuitively through mouse or touch operations. Companies widely adopt GUI in data analytics tools and business applications.
4.2 Common Examples
Typical examples of GUI include desktop operating systems, mobile apps, data dashboards, and CRM tools. GUI provides visual operability that accommodates a wide range of users.
4.3 Advantages of GUI
- Intuitive operation: Easy for beginners with visual icons.
- Immediate visual feedback: Actions like clicks and drags give instant responses.
- Accessible to a broad user base: No specialized knowledge required.
- Rich display capabilities: Organizes complex data graphically.
4.4 Disadvantages of GUI
- Resource-intensive: Requires more system resources for high-resolution graphics.
- Not ideal for complex operations: Efficiency drops when precise control is needed.
- Higher development costs: Designing visual elements takes more time and resources.
4.5 Typical Use Cases
GUI is used in data analytics tools, web apps, and customer-facing services. For instance, dashboards visualize data and support faster decision-making.
| Item | Details | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Operated visually with icons and buttons | Data analytics dashboards |
| Advantages | Intuitive, instant visual feedback, broad user base, rich display | Beginner-friendly apps |
| Disadvantages | Resource-heavy, inefficient for complex operations, costly to develop | High-spec environments required |
| Use Cases | Data analytics, customer-facing services | CRM tools |
GUI is well-suited for intuitive interactions and appeals to a wide user base. Companies should leverage GUI in tasks where user experience is critical, thereby enhancing both efficiency and satisfaction.
5. CUI (Character User Interface)
CUI is a text-based interface operated through typed commands. This section explains the characteristics of CUI in detail.
5.1 What is CUI?
CUI (Character User Interface) is an interface where users input text commands via a keyboard to perform operations. In enterprises, it is widely used for server management and script execution.
5.2 Typical Examples
CUI is found in Unix shells and legacy system terminals. It is also used for system administration tools and database operations.
5.3 Advantages of CUI
- Fast processing: No graphical rendering, runs smoothly.
- Lightweight: Operates efficiently even on low-spec environments.
- Script-friendly: Suitable for task automation.
5.4 Disadvantages of CUI
- High learning cost: Requires command knowledge, making it difficult for beginners.
- Low visual intuitiveness: Lacks visual feedback.
- Error handling challenges: Command mistakes directly cause errors.
5.5 Main Use Cases
CUI is ideal for server configuration and batch processing. For example, it is used in database management and log analysis, where fast operations are essential.
| Item | Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Text-based, command input | Unix shell |
| Advantages | Fast, lightweight, script-friendly | Low-spec environments |
| Disadvantages | High learning curve, low intuitiveness, error-prone | Not suitable for beginners |
| Use Cases | Server management, log analysis | Database operations |
CUI is effective in scenarios requiring lightweight and fast operations. Enterprises can leverage CUI in specialized tasks to improve efficiency.
6. CLI (Command Line Interface)
CLI is a UI specialized in command-line operations. This section clarifies the difference between CLI and CUI.
6.1 What is CLI?
CLI (Command Line Interface) is an interface where users input text-based instructions through the command line. It is widely adopted in enterprise development and system administration.
6.2 Difference Between CUI and CLI
- CUI: Refers broadly to any text-based UI.
- CLI: A subset of CUI, focused specifically on single command-line operations.
CLI is particularly suitable for scripting and automation, enabling technical professionals to work efficiently.
6.3 Main Use Cases of CLI
CLI is used by engineers and system administrators for scripting, automation, and server management. For instance, it supports CI/CD pipeline setup and task automation.
| Item | Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Command-line operation | Script execution |
| Advantages | Fast, automation-ready, flexible | CI/CD pipelines |
| Disadvantages | High learning cost, low intuitiveness | Not beginner-friendly |
| Use Cases | Development, system administration | Server configuration |
CLI delivers high-speed operations for specialized tasks. Companies use CLI to enhance automation and streamline development workflows, boosting productivity.
7. VUI (Voice User Interface)
VUI is an interface operated through voice commands. This section explains the key characteristics of VUI.
7.1 What is VUI?
VUI (Voice User Interface) allows users to control devices using spoken commands. With advancements in AI-powered voice recognition, VUI has spread across smart devices and business applications.
7.2 Typical Examples
VUI is found in smart speakers and mobile assistants. It is also being adopted in enterprise apps for voice-based operations and customer support.
7.3 Advantages of VUI
- Hands-free operation: Usable even when the user’s hands are occupied.
- Intuitive interaction: Simple control through voice instructions.
- Reduced user effort: No need for typing or clicking.
7.4 Disadvantages of VUI
- Recognition accuracy dependency: Accents or pronunciation may cause misinterpretations.
- Unsuitable for noisy environments: Performance degrades in loud surroundings.
- Privacy concerns: Voice data collection raises security and confidentiality issues.
7.5 Main Use Cases
VUI is applied in smart devices and customer support systems. For example, employees can use voice commands to search data or manage tasks within enterprise applications.
| Item | Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Operated via voice commands | Smart speakers |
| Advantages | Hands-free, intuitive, reduces workload | Voice-based data search |
| Disadvantages | Dependent on accuracy, noise-sensitive, privacy concerns | Misrecognition in noisy environments |
| Use Cases | Smart devices, customer support | Voice-controlled business apps |
VUI provides the convenience of hands-free operation. Enterprises can enhance accuracy with AI-powered voice recognition, improving efficiency in various workflows.
8. TUI (Tangible User Interface)
TUI is an interface operated through physical and tactile interaction. This section explains the characteristics of TUI.
8.1 What is TUI?
TUI (Tangible User Interface) is an interface that controls digital information by manipulating physical objects. It is increasingly used in education, art, and prototyping.
8.2 Typical Examples
TUI is found in interactive exhibits and educational blocks. In business, it is also used in interactive product demonstrations at exhibitions.
8.3 Advantages of TUI
- Tactile and intuitive: Easy to learn through physical interaction.
- Creative experiences: Provides unique experiences in education and art.
- Interactivity: Promotes direct engagement between users and systems.
8.4 Disadvantages of TUI
- High implementation cost: Requires development of physical devices.
- Low versatility: Often limited to specific applications.
- Maintenance burden: Physical components require upkeep.
8.5 Main Use Cases
TUI is applied in educational tools and exhibitions. For example, businesses use it for product design prototyping and interactive demos at trade shows.
| Item | Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Operated via physical objects | Educational blocks |
| Advantages | Intuitive, creative, interactive | Tactile learning |
| Disadvantages | High cost, low versatility, maintenance required | Limited to specific applications |
| Use Cases | Education, exhibitions | Product demos |
TUI provides hands-on, tactile experiences. Companies can leverage TUI in education and prototyping to deliver unique user experiences.
9. NUI (Natural User Interface)
NUI is an interface operated through natural human actions. This section highlights its features.
9.1 What is NUI?
NUI (Natural User Interface) is an interface that uses gestures and motions for interaction. With the advancement of AI and sensor technology, it has become popular in AR/VR environments.
9.2 Typical Examples
NUI is found in gesture-controlled games and AR/VR applications. In business, it is applied in virtual environment operations and design simulations.
9.3 Advantages of NUI
- Natural interaction: Operated intuitively through gestures.
- High immersion: Provides realistic experiences in AR/VR.
- Intuitive learning: Easier learning through body movement.
9.4 Disadvantages of NUI
- Complex implementation: Requires advanced sensor technologies.
- Accuracy issues: May result in misrecognition.
- High cost: Development and devices are expensive.
9.5 Main Use Cases
NUI is applied in AR/VR apps and interactive exhibitions. For instance, it is used in virtual product design simulations and immersive training programs.
| Item | Content | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Operated through gestures and motion | AR/VR apps |
| Advantages | Natural interaction, immersive, easy to learn | Virtual simulation |
| Disadvantages | Complex implementation, accuracy challenges, costly | Risk of misrecognition |
| Use Cases | AR/VR, exhibitions | Design simulations |
NUI offers highly immersive experiences. Companies can adopt NUI in AR/VR and prototyping to deliver advanced and innovative user interfaces.
Conclusion
The different UI types (GUI, CUI, CLI, VUI, TUI, NUI) each have unique features and use cases, contributing to operational efficiency and enhanced user experiences. Businesses can boost productivity by selecting the most suitable UI for their needs, considering usability and learning costs for data analysis and system management.
By incorporating AI-driven user testing and improving accuracy, organizations can prepare for the future evolution of UI. Start by experimenting with the UI that best fits your business needs to improve user experience.


 EN
EN JP
JP KR
KR