SaaS: Empowering Businesses with Flexible and Scalable Software Solutions
Software as a Service (SaaS) applications have gained tremendous popularity in recent years, revolutionizing the way businesses access and utilize software. By offering cloud-based solutions, SaaS applications provide numerous benefits, including cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of use.
In this article, we will explore the concept of SaaS applications, their advantages, popular use cases, and considerations for businesses when adopting such solutions.
1. Understanding SaaS Applications
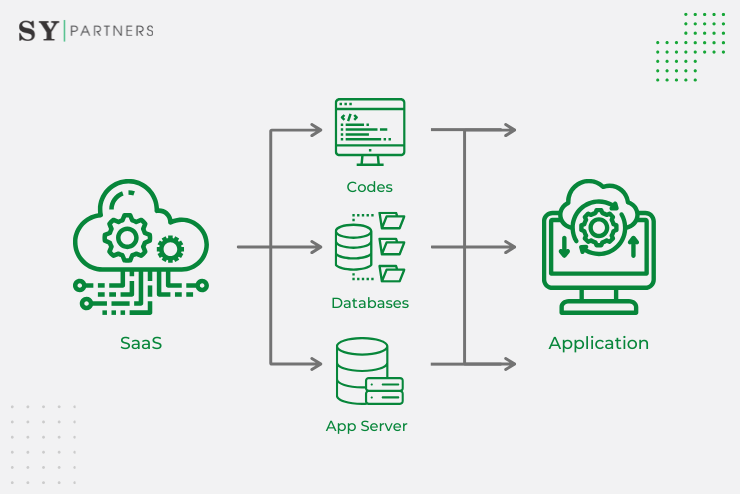
SaaS applications, also known as cloud applications, are software solutions that are centrally hosted and delivered over the internet. Instead of installing and running applications locally, users can access and use these applications through a web browser or API, eliminating the need for complex installations and maintenance.
2. Key Characteristics of SaaS Applications
2.1 Centralized Hosting
SaaS applications are hosted on the service provider's infrastructure, which typically includes servers, databases, and networking components. This centralized hosting allows users to access the application from anywhere with an internet connection, enabling remote work and collaboration.
2.2 Subscription-Based Model
SaaS applications follow a subscription-based pricing model, where users pay a recurring fee based on usage or the number of users. This model offers cost predictability and scalability, as businesses can adjust their subscription plans as their needs evolve.
2.3 Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Service providers are responsible for maintaining and updating the SaaS applications. This ensures that users always have access to the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches without the need for manual updates or disruptions to workflow.
2.4 Multi-Tenancy
SaaSapplications are designed to support multiple tenants, enabling a single instance of the application to serve multiple customers or organizations. This multi-tenancy architecture allows for efficient resource utilization, cost savings, and easy customization for individual tenants.
3. Advantages of SaaS Applications
3.1 Cost-Effectiveness
SaaS applications eliminate the need for businesses to invest in hardware, software licenses, and infrastructure. Instead, they can access the software through a subscription, reducing upfront costs and allowing for predictable budgeting. Additionally, businesses can scale their usage up or down as needed, paying only for what they use.
3.2 Scalability and Flexibility
SaaS applications offer scalability, allowing businesses to easily adjust their usage based on demand. As organizations grow or experience seasonal fluctuations, they can quickly scale up resources to accommodate increased usage. Conversely, they can scale down during periods of lower demand, avoiding unnecessary costs.
3.3 Accessibility and Collaboration
SaaS applications are accessible from any device with an internet connection, enabling users to work from anywhere, anytime. This accessibility promotes remote work, enhances collaboration among teams, and facilitates real-time data sharing and updates.
3.4 Rapid Deployment
SaaS applications can be quickly deployed without the need for complex installations and configurations. Users can simply sign up for the service, and the application is ready to use. This accelerated deployment allows businesses to start using the software immediately, reducing time-to-value.
4. Popular Use Cases of SaaS Applications
4.1 Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
SaaS CRM applications, such as Salesforce, provide businesses with a centralized platform to manage customer interactions, sales pipelines, and marketing campaigns. These applications enable organizations to streamline their customer management processes, improve customer satisfaction, and drive sales growth.
4.2 Human Resources (HR) and Talent Management
SaaS HR applications, like Workday or BambooHR, offer comprehensive solutions for managing employee data, recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and payroll. These applications simplify HR processes, enhance workforce productivity, and ensure compliance with regulations.
4.3 Collaboration and Communication
SaaS collaboration tools, such as Microsoft Teams or Slack, facilitate seamless communication, file sharing, and project management across teams and departments. These applications break down communication barriers, increase productivity, and foster collaboration in remote or distributed work environments.
4.4 Financial Management
SaaS financial management applications, like QuickBooks or Xero, provide businesses with tools for accounting, invoicing, expense management, and financial reporting. These applications streamline financial processes, improve accuracy, and provide real-time insights into business performance.
5. Considerations for Adopting SaaS Applications
5.1 Data Security and Privacy
When adopting SaaS applications, businesses should carefully evaluate the service provider's security measures, data encryption protocols, and compliance certifications to ensure the protection of sensitive data. It is essential to choose reputable providers that prioritize data security and offer robust privacy controls.
5.2 Integration Capabilities
Consider whether the SaaS application can integrate with existing systems and workflows. Seamless integration allows for data exchange, process automation, and a cohesive user experience. Compatibility with other essential tools and platforms is crucial for maximizing the value of the SaaS application.
5.3 Vendor Reliability and Support
Evaluate the reliability and track record of the SaaS provider. Consider factors such as service uptime, customer support responsiveness, and service level agreements (SLAs). Reliable support and timely issue resolution are vital for minimizing disruptions and ensuring a smooth user experience.
Conclusion
SaaS applications have transformed the way businesses access and utilize software, offering cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of use. With centralized hosting, automatic updates, and subscription-based pricing, SaaS applications provide businesses with flexible and accessible software solutions.
By leveraging SaaS applications in various domains, organizations can streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and drive productivity. However, it is essential to carefully consider factors such as data security, integration capabilities, and vendor reliability when adopting SaaS applications to ensure a successful implementation and maximize the benefits for the business.


 EN
EN JP
JP KR
KR