Cloud Security in 2025: Key Risks & Mitigations
As digital transformation accelerates, cloud computing has become the backbone for many enterprises, enabling efficient data storage and processing. However, with the expansion of cloud infrastructure and services, cloud security risks have grown more sophisticated and complex.
This analysis delves into the top cloud security threats in 2025 and provides comprehensive solutions to safeguard your systems effectively.
1. Overview of Cloud Security in 2025
By 2025, cloud adoption is projected to surge, with a majority of global enterprises leveraging multiple cloud services. While the cloud offers significant benefits, it also introduces new security challenges that organizations must address to protect their data and operations.
1.1. Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Cost Optimization
Cloud services reduce the need for substantial capital investments in physical infrastructure and lower ongoing maintenance expenses.
- Scalability and Flexibility
Businesses can rapidly adjust resources based on demand, helping maintain optimal performance without excessive provisioning.
- Rapid Deployment
Cloud platforms enable faster deployment of applications and services, enhancing time-to-market and agility.
1.2. Security Challenges in the Cloud
Despite its advantages, cloud computing brings unique security vulnerabilities that can impact business continuity:
- Increased Complexity
Managing multiple cloud services and configurations can make it challenging to maintain consistent security policies.
- Advanced Attack Vectors
Cybercriminals are developing increasingly sophisticated methods to exploit cloud weaknesses, requiring robust defense strategies.
2. Top Cloud Security Risks in 2025
Leading cybersecurity firms such as McAfee and Palo Alto Networks highlight the most critical cloud security threats that organizations must address:
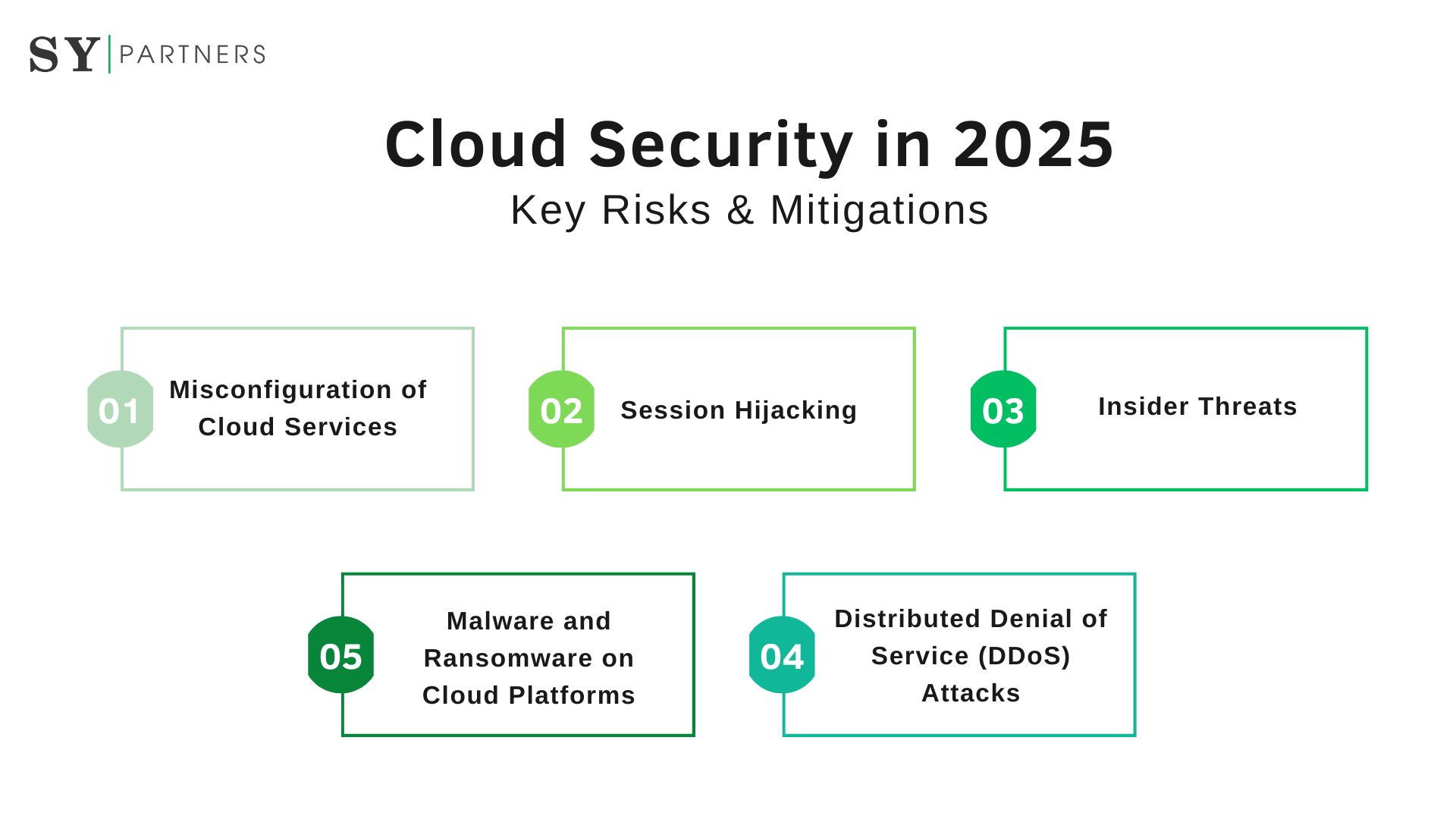
2.1. Misconfiguration of Cloud Services
- Description
Improperly configured cloud services—e.g., public-facing storage buckets or weak firewall rules—can expose sensitive data and internal systems.
- Consequences
- Data Breach: Sensitive information may be inadvertently disclosed or stolen.
- System Compromise: Attackers can infiltrate networks, deploy malware, or disrupt operations.
2.2. Session Hijacking
- Description
Attackers intercept legitimate user sessions to gain unauthorized access to cloud resources.
- Consequences
- Unauthorized Access: Hijacked sessions can be used to manipulate data, steal information, or escalate privileges.
- Operational Disruption: Malicious activities can cause downtime, leading to potential revenue loss and reputational damage.
2.3. Insider Threats
- Description
Employees or partners with valid access to cloud systems may intentionally or unintentionally misuse their privileges or leak sensitive data.
- Consequences
- Reputational Damage: Data leaks erode customer trust and damage the organization’s public image.
- Financial Costs: Responding to and remediating insider breaches can be expensive, involving legal fees and operational disruptions.
2.4. Malware and Ransomware on Cloud Platforms
- Description
Attackers leverage cloud services to spread malware or encrypt data with ransomware. New variants continuously evolve, targeting stored and in-transit data.
- Consequences
- Data Encryption or Theft: Critical information may be locked or stolen, causing significant downtime and impacting business continuity.
- Financial Burden: Ransom payments, system restoration, and potential loss of revenue can be costly.
2.5. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
- Description
Attackers flood cloud resources with excessive traffic, rendering applications or websites inaccessible.
- Consequences
- Service Downtime: Extended outages can result in lost sales and decreased customer satisfaction.
- Reputational Harm: Frequent DDoS attacks can undermine an organization’s reliability and market standing.
3. Effective Solutions to Protect Cloud Systems
To counter these cloud security risks, organizations must implement a comprehensive security strategy combining processes and technology:
3.1. Standardized Security Configurations
- Implement Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
CSPM tools automatically assess and monitor cloud settings, alerting administrators to risky configurations. Solutions like Prisma Cloud or Azure Security Center can help maintain continuous compliance.
- Least Privilege Access Policies
Only grant users the minimum necessary permissions to fulfill their roles. This reduces the risk of privilege misuse or escalation.
3.2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) & Session Management
- Require MFA
Multiple authentication factors significantly decrease the likelihood of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
- Session Timeout Policies
Enforce automatic logouts after periods of inactivity, preventing attackers from hijacking unattended sessions.
3.3. Enhanced Monitoring and Threat Detection
- Deploy SIEM/SOAR Solutions
Tools like Splunk, IBM QRadar, or Palo Alto Networks Cortex XSOAR collect and analyze logs, detecting anomalous behavior and facilitating swift incident response.
- Insider Threat Monitoring
Track and analyze user activities to identify unusual access patterns, helping to detect and block malicious or negligent insiders.
3.4. Data Encryption and Regular Backups
- Encryption at Rest and In Transit
Use strong encryption (e.g., AES-256) to protect sensitive data from eavesdropping or theft.
- Comprehensive Backup & Disaster Recovery
Schedule frequent backups and test recovery procedures to ensure rapid restoration after ransomware attacks or system failures.
3.5. Web Application Firewalls (WAF) & Content Delivery Networks (CDN)
- Web Application Firewalls
WAFs such as AWS WAF or Cloudflare WAF filter out malicious traffic and shield applications from common exploits like SQL injection or XSS.
- CDN Adoption
Services like Cloudflare, Akamai, or AWS CloudFront distribute traffic, mitigating DDoS attacks by absorbing excessive loads and improving website performance.
4. Future Trends in Cloud Security
Entering 2025, the cloud security landscape will continue to evolve, driven by emerging trends and technological advancements:
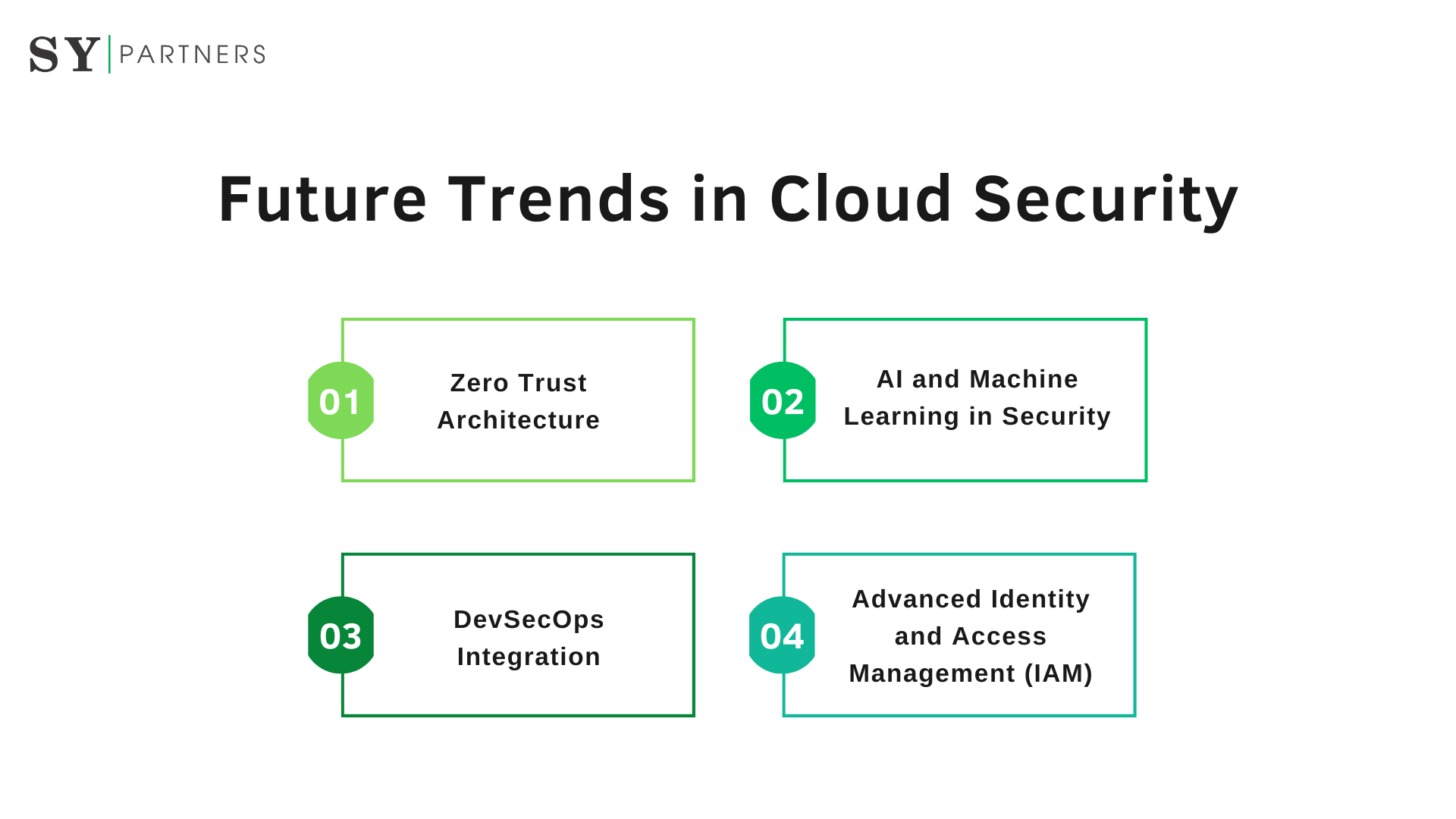
4.1. Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust remains a dominant approach, emphasizing “never trust, always verify.” It requires continuous identity verification and strict access controls, regardless of whether users are inside or outside the organization’s network perimeter.
4.2. AI and Machine Learning in Security
AI/ML-based security tools automatically detect and adapt to evolving threats, analyzing vast datasets to find anomalies, predict potential attacks, and respond proactively.
4.3. DevSecOps Integration
DevSecOps incorporates security at every stage of the software development lifecycle, aligning development, operations, and security teams. Key practices include shift-left security, automated compliance checks, and collaborative incident response.
4.4. Advanced Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM solutions are increasingly leveraging features like biometric authentication, behavioral analytics, and privileged access management to ensure that only authorized users can access critical systems and data.
5. Conclusion
In 2025, cloud security risks will become increasingly complex, posing significant challenges for organizations. However, by adopting a comprehensive security strategy and implementing robust technological solutions, businesses can effectively minimize and manage these threats. Key takeaways include:
- Enforcing Standardized Configurations and Continuous Monitoring
- Implementing MFA and Least Privilege Policies
- Using Strong Encryption and Maintaining Regular Backups
- Deploying Advanced Security Tools (SIEM/SOAR, WAF, etc.)
Cloud security is an ongoing journey requiring regular updates, vigilance, and responsiveness to new threats. By staying proactive and embracing modern security trends, organizations can protect their cloud infrastructure and maintain resilience in an ever-evolving digital environment.


 EN
EN JP
JP KR
KR