Edge Computing: Revolutionizing Data Processing and Connectivity
In today's rapidly advancing digital era, where data generation and consumption are skyrocketing, traditional cloud computing models are facing significant challenges. The ever-growing demand for real-time processing, low-latency applications, and data security concerns has paved the way for a transformative technology known as edge computing.
In this article, we will explore the concept of edge computing, its advantages, applications across various industries, and its potential to revolutionize the digital landscape.
1. What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing can be defined as a decentralized computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, enabling real-time data processing and analysis at the "edge" of the network. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which relies on centralized data centers, edge computing leverages a distributed network of edge devices located in close proximity to the data sources.
2. Advantages of Edge Computing
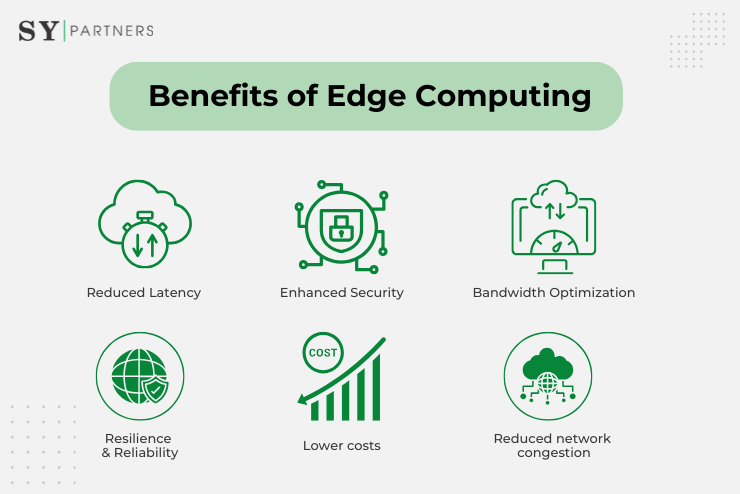
2.1 Reduced Latency
By processing data closer to the edge devices, edge computing significantly reduces latency, ensuring faster response times and improved user experiences. This is particularly crucial for applications requiring real-time interactions, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality.
2.2 Enhanced Security
Edge computing addresses security concerns by minimizing data transmission to the cloud. Instead of sending sensitive information to a remote server, data can be processed and analyzed locally, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring data integrity.
2.3 Bandwidth Optimization
With the exponential growth of data, transmitting all information to a central server for processing can strain network bandwidth. Edge computing alleviates this burden by performing data processing and filtering at the edge, sending only the relevant information to the cloud, thereby optimizing bandwidth usage.
2.4 Resilience and Reliability
Edge computing enhances the resilience and reliability of applications by reducing reliance on a single point of failure. In the event of network disruptions or connectivity issues, edge devices can continue to operate autonomously, ensuring uninterrupted services.
3. Applications of Edge Computing
3.1 Internet of Things (IoT)
Edge computing plays a vital role in IoT deployments. By enabling localized data processing and analysis, it supports real-time decision-making in smart homes, cities, and industrial IoT applications. Edge devices can collect, process, and analyze sensor data, allowing for faster response times and reducing the need for constant cloud connectivity.
3.2 Autonomous Vehicles
Edge computing is reshaping the automotive industry by enabling autonomous vehicles to make split-second decisions without relying on distant cloud servers. By leveraging powerful edge devices installed within vehicles, critical data processing, object detection, and decision-making can occur in real-time, ensuring safe and efficient transportation.
3.3 Healthcare
Edge computing offers transformative possibilities in healthcare. From wearable devices that monitor vital signs to remote patient monitoring systems, edge computing enables real-time data analysis, facilitating quicker diagnosis, personalized treatments, and improved patient outcomes. It also addresses privacy concerns by keeping sensitive medical data within local networks.
3.4 Retail and Customer Experience
Edge computing empowers retailers to deliver personalized and immersive customer experiences. By leveraging edge devices, retailers can analyze customer data in real-time, offer personalized recommendations, and create interactive augmented reality experiences without latency issues, enhancing customer satisfaction and driving sales.
4. The Future of Edge Computing
As technology continues to advance, edge computing is poised to play an increasingly vital role in our digital landscape. The proliferation of 5G networks, the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the ever-expanding Internet of Things will further fuel the adoption and evolution of edge computing.
We can expect to see innovative applications and a growing ecosystem of edge devices, enabling unprecedented levels of connectivity, efficiency, and intelligence.
Conclusion
Edge computing represents a paradigm shift in the way we process, analyze, and utilize data. Its ability to bring computation closer to the data source offers numerous benefits, including reduced latency, enhanced security, bandwidth optimization, and improved resilience.
With diverse applications across industries such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, healthcare, and retail, edge computing is set to revolutionize the digital landscape, empowering businesses and individuals with faster, more secure, and intelligent experiences. As we venture into an increasingly connected future, edge computing stands as a testament to our ongoing pursuit of efficiency, innovation, and a smarter world.


 EN
EN JP
JP KR
KR






